Computing History Timeline
1989 World Wide Web
Invented by Tim Berners-Lee
Table of Contents
Advantages of the World Wide Web
Disadvantages of the World Wide Web
What is the World Wide Web?
 The World Wide Web is often abbreviated to WWW. It is the
universe of network-accessible information of human knowledge.
The World Wide Web is often abbreviated to WWW. It is the
universe of network-accessible information of human knowledge.
It is a system of interlinked, hypertext documents accessed through the Internet. It was created by Sir Timothy Berners-Lee in 1989. The World Wide Web contains web pages that are created by anybody using a web browser. These web pages contain detailed text, images, videos and other multimedia that can navigated, browsed and contributed to by other people.
Tim Berners-Lee, a scientist, invented the World Wide Web in 1989. He worked at CERN (largest Internet node in Europe) where he proposed a project based on the concept of hypertext, to assist in sharing and updating information among researchers. He built a prototype system called ENQUIRE. Tim later took these ideas by joining hypertext and Internet to create the World Wide Web.
How the World Wide Web works?
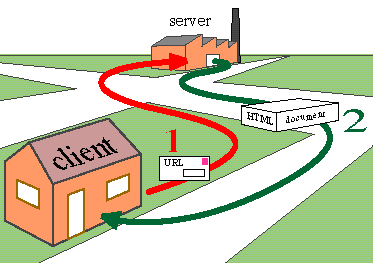
After the creation of the World Wide Web, this produced a powerful and easy to use global information system available at the click of a mouse. To use the Web, you need computer, a connection to the Internet and a browser.
To view a web page on the World Wide Web takes six steps
Step One: All web servers have an IP (internet provider) address. For e.g. 255.255.255.255.10
Step Two: The server must store all these IP address in its database
Step Three: Once the user types in the URL into the browser, the URL is resolved into an IP address
Step Four: The browser then requests that particular IP address from the web server
Step Five: The web server then looks for that particular IP address
Step Six: After the IP address is found, the web page is shown to the user. Any attachment files and images will be shown as well to produce the on-screen web page that the user sees.
Advantages of the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web has many advantages in comparison to other hypertext systems back then. The Web required only unidirectional links rather than bidirectional links. This made it possible for someone to link to another resource without action by the owner of that resource.
It is relatively cheap and is applicable to any operating system e.g. Windows, Apple, Linux, etc. It also is an easy to use multilingual web that provides multimedia e.g. video, text, images, etc. Communication is fast and reliable. It provides such a wide range of information that literally anyone can find the Web useful. It provides things such as communication, an online dictionary, global news, history, sport, music, etc.
Disadvantages of the World Wide Web
There are many disadvantages of the web that may include security e.g. hacking, copyright plagiarism, etc. There may be information which has not been edited or proven, connection and download time may be extremely slow and volatility of file location and availability.
History
The World Wide Web began as a networked information project at CERN (the largest internet node in Europe), where Tim Berners-Lee, a scientist, developed a vision of the project.
 The basic idea of the World Wide Web was to merge the
technologies of personal computers, computer networking and hypertext into a
powerful and easy to use global information system.
The basic idea of the World Wide Web was to merge the
technologies of personal computers, computer networking and hypertext into a
powerful and easy to use global information system.
Basic ideas about creating the web can be dated back to as far as 1980 where Tim Berners-Lee built a prototype system called ENQUIRE which was an information management system.
Later down the track, on March 1989, Tim Berners-Lee wrote a proposal to develop another information management system that was similar but much more complex than ENQUIRE.
 On 12 November 1990, Tim Berners-Lee and Robert Cailliau
wrote a proposal for the development of the World Wide Web. By Christmas 1990,
Tim Berners-Lee had used a NeXTcube as the world’s first web server, web browser
and web pages.
On 12 November 1990, Tim Berners-Lee and Robert Cailliau
wrote a proposal for the development of the World Wide Web. By Christmas 1990,
Tim Berners-Lee had used a NeXTcube as the world’s first web server, web browser
and web pages.
On 6 August 1991, after Tim Berners-Lee posted a short summary of the World Wide Web project on the web it marked the Web as a publicly available service on the Internet.
CERN announced that the World Wide Web would be free to anyone along with no fees charged by 30 April 1993. This allowed the Web to become the most popular Internet protocol by 1993.
Biliography
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Wide_Web#History
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tim_Berners-Lee
http://public.web.cern.ch/PUBLIC/en/About/WebStory-en.html
by Molis Nou


